What is andropause?
As men approach middle age and beyond (40 and older) they may experience a phenomenon similar to female menopause, called Andropause. Andropause also referred to as "male menopause" is the term that describes the hormonal changes that occur in the body of a middle age man.
What happens during andropause?
Decline in production of male hormones such as testosterone and DHEA. (This decline of male hormones during andropause occurs in a more subtle way then the hormonal decline during female menopause).
The decrease of testosterone and DHEA creates health risks and greater exposure to many health conditions, such as increased risk for cardiovascular disease (including heart attack, stroke and hypertension), decline in memory and brain function, decreased muscle mass, increased fat tissue as well as osteoporosis.
What are the symptoms of andropause?
- Decreased energy
- Lack of libido
- Prostate hypertrophy
- Memory impairment
- Irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Hot flushes
Bio-identical hormone replacement therapy, using bio-identical testosterone and bio-identical DHEA will help to alleviate the unpleasant andropause symptoms. Above all, utilizing bio-identical hormone replacement therapy for the treatment of andropause provides protective health benefits for an aging man, by restoring vitality, enhancing sexual function, improving cardiovascular function, reducing high blood pressure, improving memory and brain function as well as reducing the risk for degenerative diseases.
What is Testosterone?
- Steroid hormone from the androgen group.
- Principal male sex hormone
- It is primarily secreted in the testes of males and the ovaries of females
- Small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands.
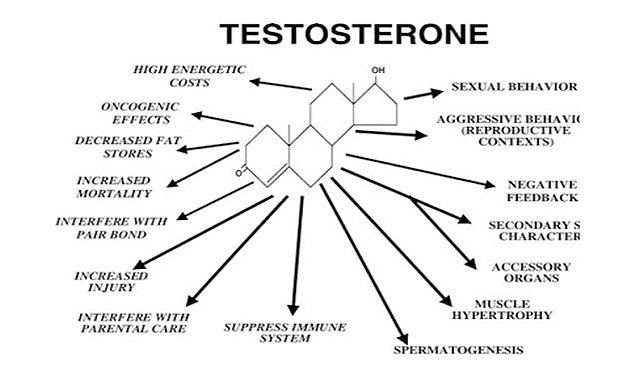
What are the functions of Testosterone?
- In men, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as the testis and prostate.
- Responsible for the proper development of male sexual characteristics.
- Promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass, hair growth and deepening of the voice.
- Essential for health and well-being as well as preventing osteoporosis.
- Essential for maintenance of adequate levels of red blood cells, sense of well-being, and sexual and reproductive function.
"Inadequate testosterone production is not a common cause of erectile dysfunction (ED). When ED does occur with decreased testosterone production, testosterone replacement therapy may improve the ED."
What causes testosterone deficiency?
As a man ages, the amount of testosterone in his body gradually declines. This natural decline starts after age 30 and continues throughout his life. The significance of this decline is controversial and poorly understood. Among other potential causes of testosterone deficiencies are:
- Injury or infection to the testicles
- Chemotherapy or radiation treatment for cancer
- Genetic abnormalities such as Klinefelter's Syndrome (extra x chromosome)
- Hemochromatosis (too much iron in the body)
- Dysfunction of the pituitary gland (a gland in the brain that produces many important hormones)
- Medications, including hormone analogues used to treat prostate cancer and steroids
- Chronic illness
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Chronic renal (kidney) failure
- AIDS
- Inflammatory disease such as sarcoidosis (a condition that causes inflammation of the lungs and other organs)
- Stress
- Alcoholism
- Congenital conditions, Kallman's Syndrome (low hormones, inability to smell and other abnormalities)
Important points to take note about male testosterone levels
- Testosterone fluctuates considerably from week to week and even from day to day. Stress, lack of sleep and many other things that are a normal part of life can affect testosterone levels.
- Get your testosterone levels read in the morning if at all possible.
- Male testosterone levels peak in the morning and then steadily decrease until late evening. This decline from am to pm is, on average, about 35% for mostly the younger guys and about 10% for seniors.
- If you are eating a low fat or vegetarian diet, your testosterone levels may be lower than the typical male omnivore.
However, this isn't a bad thing for vegetarians because of the excellent health outcomes; it boosts nitric oxide (the key target of all major pharmaceutical treatments for ED) levels so powerfully even though your testosterone levels are lower than a meat eater.
What are the symptoms of testosterone deficiency?
- Decreased sex drive
- Decreased sense of well-being
- Depressed mood
- Difficulties with concentration and memory
- Erectile dysfunction (Inability to achieve or sustain an erection suitable for sexual intercourse)
What happens during testosterone deficiency?
- Decrease in muscle mass, with an increase in body fat
- Variable effects on cholesterol metabolism
- A decrease in hemoglobin and possibly mild anemia
- Fragile bones (osteoporosis)
- A decrease in body hair
As men enter middle age, they may observe changes in regard to a corresponding decrease in testosterone like infrequent erections, fatigue, thinning of the skin, decrease in muscle mass and strength and more body fat. This hormonal decline that occurs with the changes of aging has led many men to seek testosterone replacement therapy.
What is Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
Testosterone or Androgen replacement therapy is a hormone treatment often prescribed to:- Reverse the effects of male hypogonadism (reduction or absence of hormone secretion or other physiological activity of the testes).
- Lower the effects or restrain the onset of normal male aging.
- Also used for men who have lost their testicular activity through illnesses, cancer, or other causes.
"The doses used in testosterone replacement therapy are certainly safe because they only achieve physiologic (natural) levels of hormone in the blood."
Available Form
Testosterone creams; bio-identical
Testosterone peaks during adolescence and early adulthood. As you get older, your testosterone level gradually declines about 1 percent a year after age 30. While this is a fact of life for most all men, it is important to determine in older men if a low testosterone level is simply due to the decline of normal aging or if it is due to a disease (hypogonadism). However, this does not mean there is nothing men can do to replace the testosterone they have lost. Testosterone replacement therapy aids in increasing testosterone levels in men. In fact, there are several lifestyle tips which also help to raise testosterone levels in men when taken together with testosterone replacement therapy.
- Get Rid of Excess Body Fat According to Dr. Joseph Zmuda, an epidemiologist at the University of Pittsburg, men who have excess body fat are exposed to elevated estrogen levels, which in sequence can decrease testosterone levels. Getting rid of excess body weight can help to lower the estrogen in men, thus increasing his testosterone levels.
- Zinc Consume foods that are rich in zinc because zinc inhibits the enzyme aromatase from turning testosterone into estrogen.
- Alcohol Decrease the amount of alcohol intake because alcohol prevents estrogen from being eliminated from the bloodstream. The more estrogen deposited in the body, the lower the testosterone levels are present. Also, alcohol decreases the amount of zinc in the body, a mineral that is vital to replacing testosterone.
- Eggs and Whey The protein in eggs and whey can help to increase testosterone levels because they contain hydrolysates. Hydrolysates are high in dipeptides and tripeptides, both of which are not digested and instead travel straight to the liver where they boost the production of the anabolic hormone insulin growth factor 1. This in turn helps to build muscle and reduce the percentage of fat in the body.
Who shouldn't take testosterone replacement therapy?
Testosterone replacement therapy may stimulate growth of the prostate. If early prostate cancer is present, testosterone may stimulate the cancer's growth. Therefore, men who have prostate cancer should not take testosterone replacement therapy. It is important for all men considering testosterone replacement therapy to undergo prostate screening before starting this therapy.
Although it is a rare condition, men who have breast cancer should not take testosterone replacement therapy.
If you are taking any hormone replacement therapy, regular follow-up appointments with your physician are important.
Testosterone in female
Many women do not know that they also produce testosterone like men. Testosterone is produced in both their ovaries and adrenal glands.
Formerly, little was known about the function of testosterone in the female body, as many scientists and doctors thought that the female hormones like estrogen and progesterone were more important.
Many analysis are now showing that normal testosterone levels are not only essential in maintaining men's health, but for women as well particularly for staying sexually active, slim and healthy. Testosterone also boosts a sense of well-being among women.
Normal range of testosterone in women
The normal values are as reference range. These ranges vary from lab to lab, and your lab may have a different range for what's normal. Your lab report should contain the range your lab uses. Also, your doctor will evaluate your results based on your health and other factors. This means that a value that falls outside the normal values may still be normal for you or your lab.
Just like in men, women's testosterone levels will peak when they are in their 20s and decrease consequently. Complications arise when testosterone levels decreases, leading to reduced motivation, fatigue, and low sex drive.
Benefits of testosterone
Testosterone therapy for men may do the same for women, especially for those who have undergone menopause or hysterectomies (surgical removal of the uterus).
A comprehensive article in 1999 by Dr. Susan Davis, a researcher of women's health issues, unveiled that a suitable testosterone therapy in women who were post-menopausal or had had their ovaries removed generated an absolute and constant progress in libido.
There are some women who may have low testosterone even though they have not gone through menopause yet, and still have their uterus and ovaries intact. This may be caused by the contraceptive pills that they are taking which eventually reduces their testosterone levels. Dr. Susan Davis proposed that testosterone therapy may benefit these women, although there's no evidence for this.
By improving libido and sexuality, women actually boost her mental and emotional health and her quality of life.
The other evident advantage of testosterone therapy in women is to manage a physically fit body structure (amount of fat and muscles in the body).
Like in men, testosterone has an effect on fat and muscle cells in a woman's body. Testosterone has the competency to act on muscle cells, making them solid and more stable.
At the same time, it also mutates specific cells (primitive cells which are capable of changing to fat, muscle or bone cells) into muscle cells instead of fat cells. Decreased testosterone levels results in more fat is accumulated, usually around the abdomen.
There are also new researches that are being carried out to determine the impacts of testosterone in women.
There are possibilities that testosterone deficiencies contributes to heart disease in post-menopausal women or women who have had their uterus and ovaries removed.
Scientists noticed that cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in post-menopausal women. At the same time, women who have undergone hysterectomies are three times more likely to develop cardiovascular disease compared to women who have not had the surgery.
Menopause and hysterectomy cause testosterone levels to decrease in a woman, although there is still not enough proof.
Low testosterone contributes to breast cancer.
Current research is also looking at the possibility that testosterone may protect against breast cancer.
A study carried out in 2000 looked at the effects of testosterone and an anti-cancer treatment on breast cell stimulation. The study found that breast cells exposed to testosterone had less significant growth.
This study correlates with another piece of research in 2003, which also showed that testosterone significantly inhibits breast cell growth, suggesting that testosterone could protect against the abnormal recurrence of cells that leads to cancer.
Testosterone therapy for women
Currently, testosterone therapy is only approved for men, so any use of it for women with low testosterone is still being tested. However, oral form of testosterone at lowest effective dose can be prescribed for menopausal women to improve libido.
Women shouldn't take testosterone therapy if they are
- Planning to, or could potentially, get pregnant.
- This is because; taking testosterone during pregnancy can cause a female fetus to develop male characteristics.
- Diagnosed with breast or uterine cancer
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease or liver disease.
If you think that you may have low testosterone levels, particularly if you have gone through menopause or a surgery to remove your uterus and/or ovaries, talk to your doctor about the role of testosterone therapy.
It is still a new concept for many doctors and patients to encounter, but do not be afraid to explore the idea, as well as to discuss the pros and cons with your doctor.





