According to FDA, adultrequires at least 4700 mg daily intake of potassium salt which is equivalent to 7-10 cups of green leafy vegetables. More often than not, measurement of potassium blood test may be inaccurate unless in extreme situation. This is becausemost potassium resides intracellularly(inside the cells). Some people may experience symptoms common to potassium deficiency but show regular levels with a potassium blood test. In this instance, doctors may order for measurement of intracellular potassium levels which can indicate deficiency sooner than ordinary blood test. However, this intracellular potassium level test may be costly and most doctorsmay be unaware of this test.
Identifying signs and symptoms of potassium deficiency isimportant because potassium is critical for normal cell function, maintaining cellular tonicity, proper nerve transmission, muscle contraction and kidney function. A systematic review concluded that high quality evidences have shown that increased potassium intake reduces blood pressure in hypertensive people (Aburto et. al., 2013). There are also moderate quality evidence reported that high potassium intake is associated with a 24% lower risk of stroke (Aburto et. al., 2013). Having adequate intake of potassium may increase muscle mass, prevent muscle loss and alsoreduce body fat.
What causes low potassium level (hypokalemia)?
- Vomiting/diarrhoea
- Keto diet
- Diuretics
- High cortisol level
- Excess water
- Hard core work out
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Excessive alcohol use
- Surgery
- Too much salt in diet
- Adrenal Stress
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Excessive laxative use
- Excessive sweating
- Folic acid deficiency
- Primary aldosteronism
- Some antibiotic use
What are the symptoms of low potassium level?
- Abnormal heart beat
- Thirst
- Depression
- Bloatedness
- High blood pressure
- Swollen ankles
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle weakness
- Sugar craving
- Constipation
- High insulin level
- Fatigue
- Low endurance
- Patient complain that they can hear their head beat
- High urination at night
- Paralysis after high carbohydrate meal
The balance between vitamin B12 and potassium (K+)
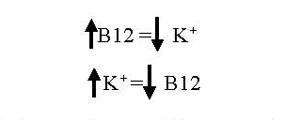
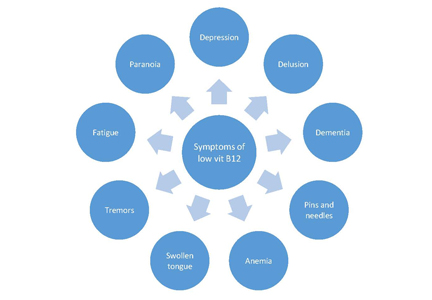
Patients who are taking potassium supplement long term are at risk for developing Vitamin B12 deficiency. Potassium is known to interfere with the absorption of Vitamin B12 and can eventually lead to the depletion of body stores of this crucial vitamin (Adv Clin Chem. 1985;24:163-216. Clinical chemistry of vitamin B12 PMID: 3911750). Vitamin B-12 can be stored in the body for very long time but not potassium. However, if the patient’s supply is interrupted long enough, a deficiency can result, which can be devastating if not recognized and treated appropriately. Figure below list out the symptoms showed in patient with low vitamin B12 level.
On the other hand, Vit B12 can also deplete potassium. How does this happen? Vit B12, together with other vitamins such as folic acid, pyridoxine and other cofactors are involved in many of the body’s function; they set the metabolism and anabolism working on a fast track. So as skin heals, muscle forms, nerves heal, and blood cells of all types are produced normally lots more potassium is used as it is one of the most common elements in EVERY cell. Thus, if not enough potassium is consumed, it will be slowly depleted.
When giving potassium and/or Vit B12 supplement one should always be wary of the effect it has on each other and also ensure a balance between the two. It is therefore advisable to ask patient to take potassium together with HMC/B12.
Sodium-Potassium ATPase (Na+-K+ pump)
The intracellular concentration of potassium is about 30 times higher compared to extracellular level and this difference forms a transmembrane electrical and chemical gradient. This electrochemical gradient allows the movement of the potassium and sodium ions in and out of the cell and it is this driving force that facilitates transport of glucose, amino acids, and other nutrients into the cell.
The ratio of potassium to sodium is 4:1.Every gram of protein will need 2.6 mg of potassium. Each glucose molecule needs 1 potassium. Without adequate intake of potassium, we will not be able to hold amino acid in our body.
In the kidney, the sodium potassium gradient is essential for it to filter waste products in the blood, reabsorb glucose and amino acid, regulate electrolyte levels in the blood and also to maintainpH. In the nervous system, Na+-K+ ATPase activity is required for firing of action potential in neurons.
Hydrogen-Potassium ATPase (H+-K+ ATPase)
Gastric hydrogen-potassium ATPases are enzyme responsible for gastric acid secretion, also referred to as proton pump. This pump plays a critical role in the production of hydrochloric acid which is essential for digestion and the maintaining of an acidic environment within the stomach.
When you should not take extra K+
- Stage IV - V kidney disease
- Addison disease
- Aldosterone deficiency
- Patients on angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers and potassium sparing diuretics
- Patient with osteoarthritis using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
References
Aburto N., Hanson S., Gutierrez H., Hooper L., Elliott P., Cappuccio F. (2013). Effect of increased potassium intake on cardiovascular risk factors and disease: systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ 346:f1378.
Bartlett E, Miller B, Thiesfeldt S, Lakhani V, Shapiro I, Sodhi K. (2018). The Role of Na/K-ATPase Signaling in Oxidative Stress Related to Aging: Implications in Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 23;19(7)
Dylewski J. and Linas S. (2018). Variability of Potassium Blood Testing: Imprecise Nature of Blood Testing or Normal Physiologic Changes? Mayo Clin Proc 93(5) 551–554.
FDA website - accessed on 14-April-2020 (https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2016/05/27/2016-11867/food-labeling-revision-of-the-nutrition-and-supplement-facts-labels#print)
Geibel J. (2005). Role of potassium in acid secretion. World J Gastroenterol 11(34): 5259-5265.
Hinderling PH. (2016). The pharmacokinetics of potassium in humans is unusual. J Clin Pharmacol 56:1212-20.
Pirahanchi Y, Aeddula N. [Updated 2020 Mar 26].Physiology, Sodium Potassium Pump (Na+ K+ Pump) In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537088/
Wang, Y., Ye, Q., Liu, C., Xie, J.X., Yan, Y., Lai, F., Duan, Q., Li, X., Tian, J., Xie, Z. (2014). Involvement of Na/K-ATPase in hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of the Src/ERK pathway in LLC-PK1 cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 71, 415-426





