What is Menopause?
Menopause is a natural biological phenomenon that all women will experience in their lifetime. The term menopause describes the alterations that generally take place in a woman's fifties or sixties, with the symptoms of change often becoming observable in her forties. During this time, the ovaries stop producing eggs, menstrual cycles become less frequent and eventually stop, and estrogen and progesterone drop. Menopause does not occur overnight, it is a gradual process. A woman is in menopause when she has had no menstrual periods (menses) for 12 months. Menopause also occurs when a woman's uterus and ovaries are surgically removed. Having a family history of early menopause, predisposes a woman to having early menopause herself. Other factors that influence the beginning time of menopause are smoking and never being pregnant.
During menopause, there will be decrease in the estrogen level which affects serotonin [ a brain (neurochemical) chemical ] which causes women to feel good, energetic and to focus more clearly. When serotonin decreases women begin to feel "blue" or experience depressive - like symptoms.
The hormonal decline that occurs with menopause causes distressing symptoms that lead many women to seek relief.
Physical Signs & Symptoms of Menopause
(Not all menopause women undergo these symptoms and are not experienced to the same range/proportion).
- Hot flushes : Sudden waves of heat that can start in the waist or chest and work their way to the neck and face and sometimes the rest of the body. They are more common in the evening and during hot weather. They can hit as often as every 90 minutes. Each one can last from 15 seconds to 30 minutes. 75 - 80 % of women of menopause experience hot flashes. Sometimes heart palpitation accompanies hot flashes.
- Irregular periods : This differs and can include:
1. Periods that gets shorter and lighter for two or more years.
2. Periods that stops for a few months and then start up again and are more widely spaced.
3. Periods that bring heavy bleeding and/or the passage of many or large blood clots. This can lead to anemia.
- Vaginal dryness : This results from hormone changes. The vaginal wall also becomes thinner. These problems can make sexual intercourse painful or uncomfortable and can lead to irritation and increased risk for infection.
- Loss of bladder tone which can result in stress incontinence (leaking urine when you cough, sneeze, laugh or exercise).
- Headaches, dizziness.
- Skin and hair changes. Wrinkled skin, growth of facial hair but thinning of hair in the temple region.
- Muscles lose some strength and tone.
- Bones become more brittle, increasing the risk for osteoporosis.
- Risk for a heart attack increases when estrogen levels drop.
The aims of bio-identical hormone replacement therapy (BIHRT) are not only to relieve displeasing symptoms of menopause, peri-menopause and andropause (male menopause), but mainly to improve, at highest quality, the youthful hormonal balance together with providing the body with the same protective health benefits that the body's own natural hormones would provide. This can be accomplished through optimization and balancing of bio-identical hormones levels in a safe, natural way. BIHRT can significantly improve the quality of life and well-being of the person for years to come.
Certified physician will establish the amount of bio-identical hormones one can take corresponding to the patient's medical history and current health problems associated to hormonal imbalance. Tests should be performed correctly to take measure of current hormone levels.
There are a few ways to use BIHRT treatment depending on symptoms. Hormones at Rxidence Compounding comprise a few formulations such as creams, capsules and suppositories. Practitioners will determine the exact amount and type of hormone, also the best supplementation method for each individual.
Emotional changes
- Irritability.
- Mood changes.
- Lack of concentration, difficulty with memory.
- Tension, anxiety, depression.
- Insomnia which may result from hot flashes that interrupt sleep.
These symptoms can seem unbearable. Women are fortunate to live today in a world which provides much guidance and many resources for understanding and managing menopause.
Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT) is known as the most effective relief to menopausal symptoms together with healthy lifestyle, social support and therapy.
Taking Estrogen and Progesterone can help alleviate the symptoms associated with approaching menopause.
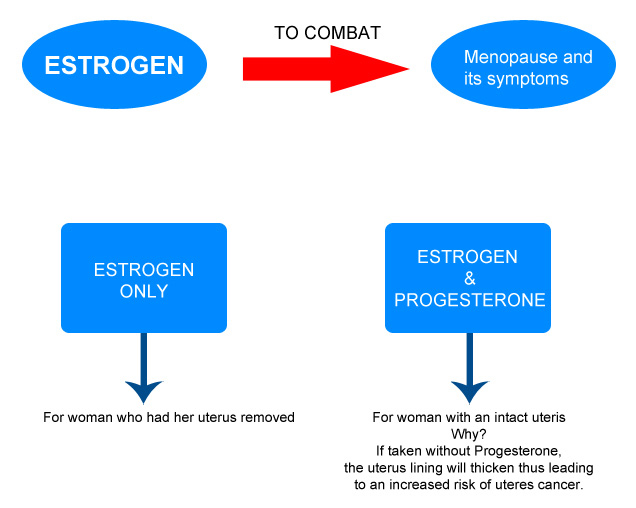
Thus BHRT often requires a combination of estrogen and progesterone. Often, women only need BHRT for a limited number of years after menopause. Estrogen can alleviate hot flashes, vaginal dryness, urinary problems, and sometimes insomnia. It can also boost a sense of well-being. Some women feel that it improves memory and concentration. BHRT can reduce the chances of osteoporosis. Estrogen may help to avoid heart disease.
Side effects of BHRT are usually minimal if physiologic (body's own dose) of hormones are balanced correctly by bio-identical ones. However, side effects certainly do not occur to all.
Estrogen Dominance (excess estrogen levels) whether the excess occurs naturally or as a result of BHRT, can be countered by body's natural mechanism of progesterone.
Studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in decreasing the risks of breast cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Heart Disease
In March 2011, the medical journal, Menopause, published the findings of The California Teachers Study (CTS), a long-term analysis surveying, measuring and observing the effects of hormone therapy whether traditional or bio-identical. The subjects, 71,000 retired female teachers between the ages of 30 and 90, were followed for nine years. The CTS study revealed that women aged 34 to 59 experienced a decreased risk of heart disease with the use of hormone therapy, while women aged 70 to 84 saw no increase in heart disease risk. In comparison to the WHI (Women's Health Initiative), the results were consistent - women of the WHI study, aged 50 to 59, also experienced a decreased risk of heart disease, while those not receiving hormone therapy experienced an increased risk.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is among the biggest concerns of women when considering whether or not to pursue hormone therapy. In 2005, the International Journal of Cancer published the results of a study out of France that tested the risk of breast cancer using various types of hormone therapy. The study concluded that little to no incidence of the disease among women who used natural (bio-identical) estrogen therapy combined with natural (bio-identical) Progesterone.





